Hyperlipidemia / Dyslipidemia
Hyperlipidemia & dyslipidemia refers to abnormalities in the levels of lipids (fats) in the bloodstream.
There are two main types of lipids i.e. cholesterol and triglycerides.
Cholesterol:
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that is found in the cells of your body and in the food you eat. There are two primary types of cholesterol:
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol: High levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease because it can deposit cholesterol in the arteries.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol: HDL cholesterol helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
Triglycerides:
Triglycerides are another type of fat found in the blood. Elevated triglyceride levels can also contribute to cardiovascular disease risk.
- Causes
- Complications & Factors
- Risks (What if its high!)
- When and who should get tested?
- What to do to mitigate high cholesterol?
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) recognize the following as major causes of high cholesterol:
- Diet: Eating a diet high in saturated and trans fats can increase cholesterol levels. Saturated fats are found in meat, poultry, dairy products, coconut, and tropical oils; and Trans fats are commonly found in fried and processed food such as margarine and baked goods.
- Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop high cholesterol due to their genes. This is called familial hypercholesterolemia or Familial hyperTriglyceridemmia
- Obesity: Excess weight can raise cholesterol levels.
- Lack of exercise: Physical activity helps to lower cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Smoking can lower HDL cholesterol and raise LDL cholesterol.
- Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism, can increase the risk of high cholesterol.
Other potential causes of high cholesterol include:
- Medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids and beta-blockers, can raise cholesterol levels.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, some women may develop high cholesterol.
- Age: Cholesterol levels tend to increase with age.
Hyperlipidemia and dyslipidemia often do not cause noticeable symptoms until they reach a critical point or lead to complications.
Research has shown that the following factors can increase the risk of high cholesterol:
- Family history: Having a parent or sibling with high cholesterol puts you at increased risk.
- Race: African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and American Indians are more likely to develop high cholesterol than white Americans.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop high cholesterol than women before menopause.
If cholesterol goes high in the body, it can build up in the walls of the arteries. This is called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis can narrow the arteries and reduce blood flow to the heart, brain, and other organs. This can lead to a number of serious health problems, including:
- Heart attack: A heart attack occurs when the blood supply to the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot.
- Stroke: A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is blocked, usually by a blood clot.
- Peripheral artery disease: Peripheral artery disease is a narrowing of the arteries in the legs and feet. It can cause pain, cramping, and numbness in the legs and feet.
- Angina: Angina is chest pain that occurs when the heart muscle does not get enough oxygen.
- Heart failure: Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
High cholesterol can also increase the risk of other health problems, such as:
- Kidney disease: High cholesterol can damage the kidneys and lead to kidney failure.
- Gallstones: Gallstones are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder. High cholesterol can increase the risk of developing gallstones.
- Dementia: High cholesterol may increase the risk of developing dementia, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
- Xanthelasma: Skin deposit of cholesterol – predominantly around the eye lid.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) and American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines to check anyone over 20yrs (In some circumstances younger patient – talk to your doctor).
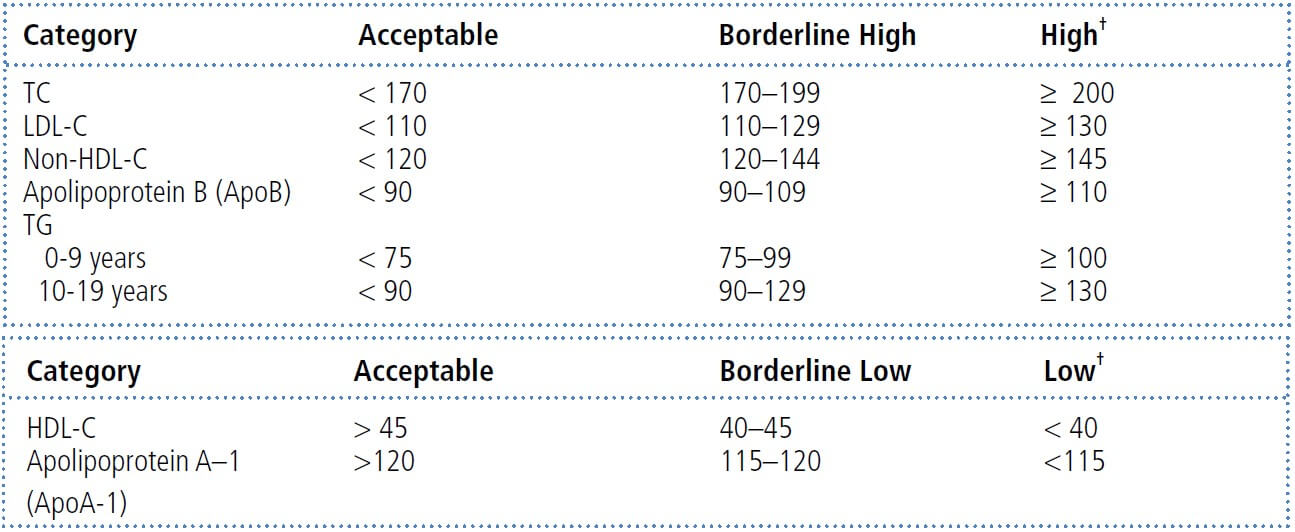
Values for plasma lipid and lipoprotein levels are from the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Cholesterol Levels in Children.
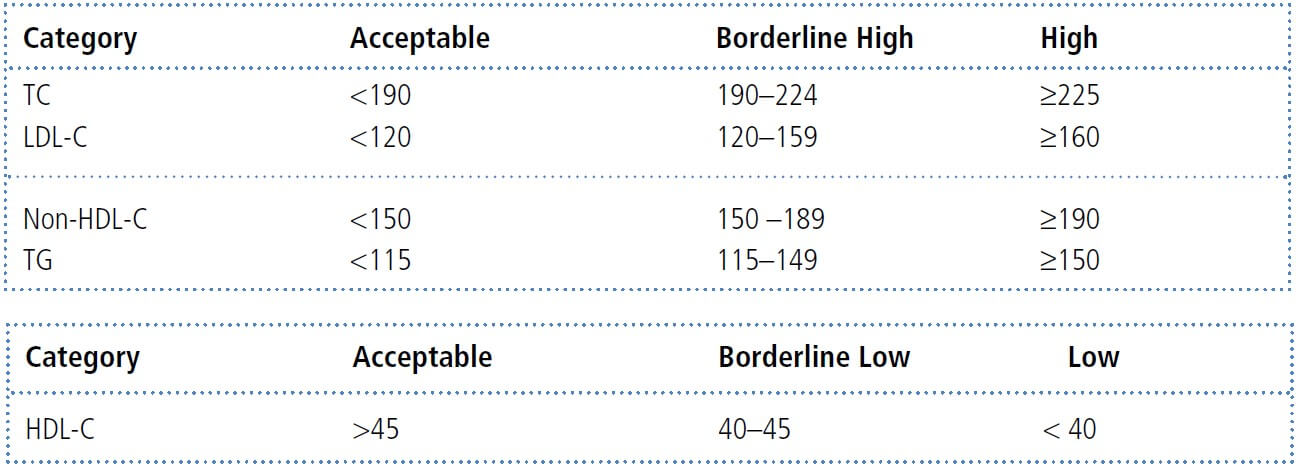 Values provided are from the Lipid Research Clinics Prevalence Study.
Values provided are from the Lipid Research Clinics Prevalence Study.
ABBREVIATION: TC: total cholesterol LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ApoB: apolipoprotein B TG: triglycerides ApoA-1: apolipoprotein A-1. NOTE: Values given are in mg/dL. To convert to SI units, divide the results for total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL–C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL–C), and non-HDL–C by 38.6; for triglycerides (TG), divide by 88.6.
Reproduced from: Daniels SR, Benuck I, Christakis DA, et al. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: Full report, 2011. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Available at: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/cvd_ped/peds_guidelines_full.pdf.
There are a number of things you can do to mitigate high cholesterol, including:
- Eat a healthy diet: This means eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also means limiting saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and added sugar.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can help to lower your cholesterol levels.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can raise LDL cholesterol and lower HDL cholesterol.
- Take cholesterol-lowering medication, if prescribed by your doctor: If lifestyle changes are not enough to lower your cholesterol levels, your doctor may prescribe medication.
- Choose lean protein sources: This includes fish, chicken, beans, and lentils.
- Limit saturated and trans fats: Eating a diet high in saturated and trans fats can increase cholesterol levels. Saturated fats are found in meat, poultry, dairy products, coconut, and tropical oils; and Trans fats are commonly found in fried and processed food such as margarine and baked goods.
- Eat plenty of soluble fiber: Soluble fiber can help to lower LDL cholesterol. Good sources of soluble fiber include oats, beans, lentils, and fruits and vegetables.
- Choose foods that are rich in plant sterols and stanols: Plant sterols and stanols can help to lower LDL cholesterol. Good sources of plant sterols and stanols include nuts, seeds, and some vegetable oils.
At Harley Street Medical Centre, our diverse team of doctors, including family medicine, cardiology, endocrinology, nephrology, internal medicine, and dietitians, combines medical expertise and advanced diagnostics to significantly enhance patients’ quality of life and overall health.

















 أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا أنقر هنا
أنقر هنا